
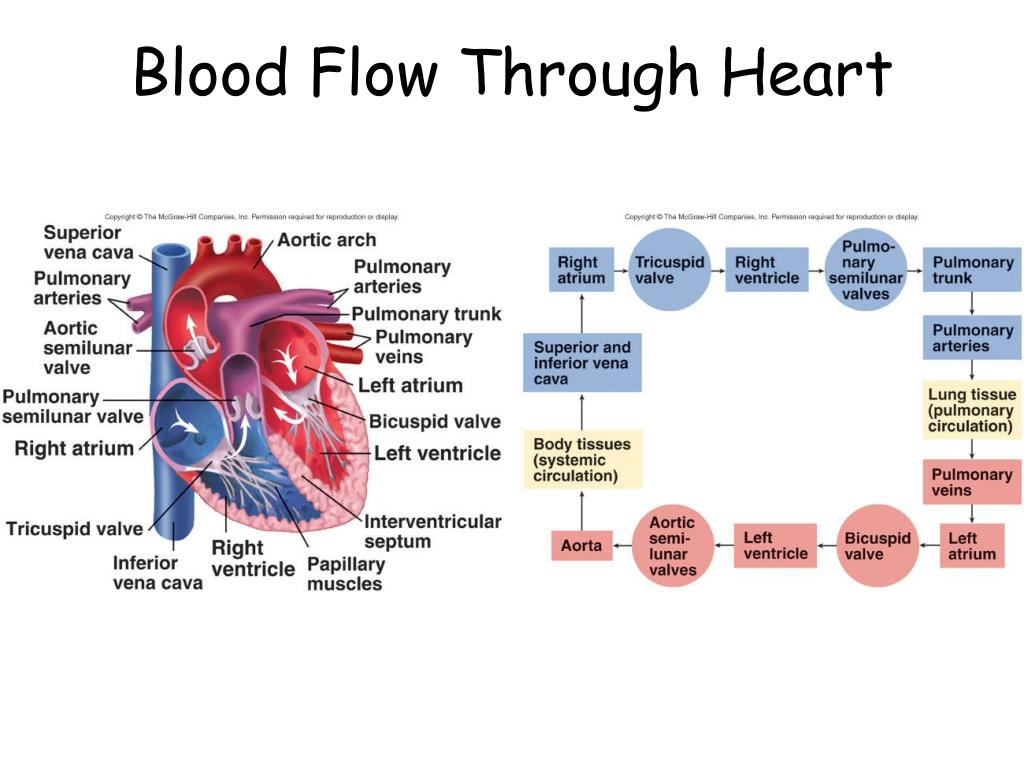
There is no backflow of blood due to the presence of the bicuspid and the tricuspid valves. This phase involves the contraction of the two auricles, pushing the blood into the respective ventricles.There are the main events in the cardiac cycle, namely: During the cardiac cycle, blood flows through the cardiac chambers in a specific manner and direction, the backward flow being prevented by the valves. This cyclical repetition is called the cardiac cycle. The changes that occur in the heart during a beat are repeated in the same order in the next beat, and the next one. The heart beats at an average rate of 70 beats per minute. The contraction and relaxation together constitute the heartbeat. The contraction of the heart is called ‘systole’ and the relaxation is called ‘diastole’. It pumps blood through the process of contraction and relaxation.

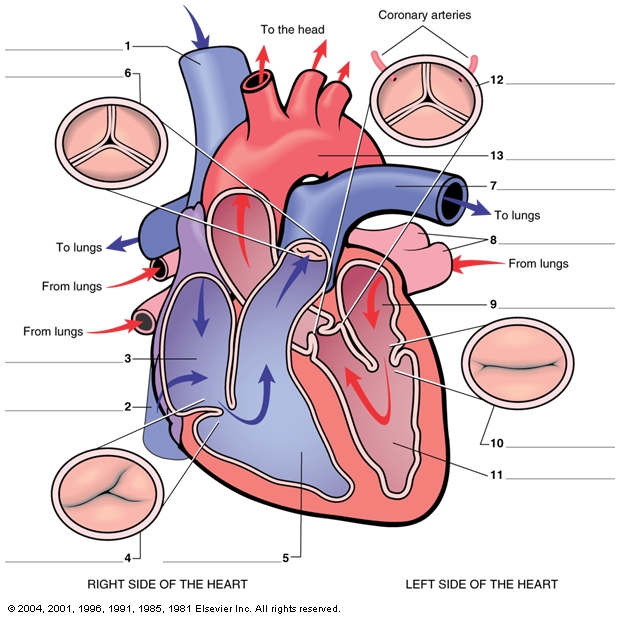
The sino-atrial node sends impulses over the two atria which are then stimulated to contract.The sino-atrial node (the pace maker) is a specialized bundle of thin, cardiac, muscular fibers buried in the right atrial wall, near the connection between the right auricle and the large veins.It has been proven that the heart continues beating regularly even after it has been disconnected from the body and the cardiac nerves. The rhythmic heart beats are actually spontaneous, as they originate from the cardiac tissue itself.The semi-lunar valve can be found where the heart connects with both the aorta and pulmonary artery.The left valve (the bicuspid valve or the mitral valve) has two flaps. The right valve (the tricuspid valve) is made up of three flaps. Blood is permitted to flow only from the atrium into the ventricle, not in the reverse direction. Each atrium is connected to its own ventricle through an opening which is guarded by a valve.The heart is divided longitudinally into two sides by means of muscular walls.They have thick, muscular walls which pump blood through the arteries. The two ventricles: these are the lower two chambers.They have thin walls which receive blood from veins. The two atria (auricles): these are the upper two chambers.The heart is divided into four chambers:.It is enclosed in the pericardium, which protects the heart and facilitates its pumping action.

The heart is a hollow muscular organ that lies in the middle of the chest cavity.Keep reading for more detailed A-level Biology revision! Summary The structure of the heart consists of four muscular chambers – the right and left atria and the right and left ventricles – which are separated by valves and blood vessels, allowing for the circulation of blood throughout the body. Which chamber receives deoxygenated blood from the body?.Which chamber of the heart pumps blood to the whole body?.What type of muscles make up the heart?.How many chambers does a human heart have?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
